INTRODUCTION
In society, thick and healthy hair is associated with good health and youth. In recent times the amount of procedures to detain hair loss has increased, but in spite of the variety available, an ideal solution doesn’t exist. Many conditions are implied, and the density, texture or colour influences the post-operative result.
The recent advances in capillary restoration techniques have been capable of creating a much more natural result than in the past. As a result, the number of patients wanting a hair transplant has increased these days.
Hair growth
Each pilose unit passes through three phases:
- Anagen, or the growth phase: 88% of the hair is in this phase. It lasts three years.
- Telogen, or the resting phase: consists of 10% of the hair. Here, the hair is not visible. This lasts for three months.
- Catagen, or the returning phase ( 2%) where around 50-100 hairs are lost daily. This lasts for three weeks.
THE FOLLICLE UNIT
This terminology describes how the hair is organized to grow on the scalp. The hair doesn’t grow evenly like corn or a cob could do, but it is organized in bunches of follicles, small isles of one to four strands of hair over the plane of the head. Each follicle unit has one different anatomical and physiological unit, and a microenvironment of cells, nerve and blood vessels.
MALE-PATTERN BALDNESS
In men who develop male-pattern baldness, hair loss can start at any given moment after puberty when the levels of androgens in the blood increase. The first change is normally a diminishing hairline in the temporal area that affects an immense majority of adults, included those who won’t suffe hair loss in the future.
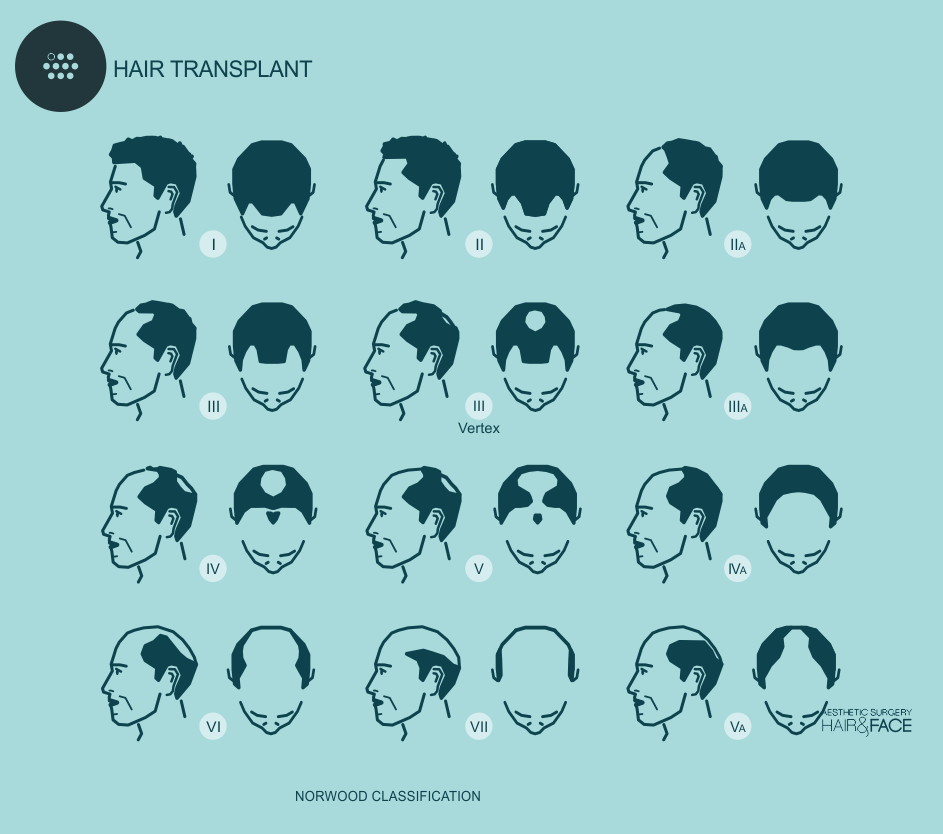
Hamilton and Norwood classified the male-pattern baldness. It was first discovered that testosterone and Dehydro-Testosterone androgens are necessary for the development of baldness. But the quantity of androgen present doesn’t necessarily have to be more than the usual for it to produce male-pattern baldness. Although the quantity of androgens is normal, if the gene of hair loss is present, there will be alopecia. Due to being an inherited condition- autosomal dominant or/and polygenic, the gene can be inherited just as much from the father as the mother. In addition, there can be a variable penetrance, of which it is impossible to predict how the extent of hair loss will be of someone by attending to their family genetic history.
FEMALE-PATTERN BALDNESS
In women just like in men, the most probable cause of hair loss of the scalp is androgenetic alopecia, which consists of hereditary sensitivity to the effects of masculine hormones over the hair follicles. There are varying severity amongst female-patterns of androgenetic alopecia and above all in its relation with masculinity. It is very rare in women to produce the billard ball effect as it is frequently seen in men.
The typical pattern entails diffuse thinning of the hair and it can vary in respect to the affected area, from the back part to the front.
MEDICATIONS THAT CAN PROVOKE ALOPECIA
Excess of vitamin A
Retinoids
Anticoagulants
Antithyroid
Allopurinol
Propranolol
Indomethacin
Amphetamins
Colchicine
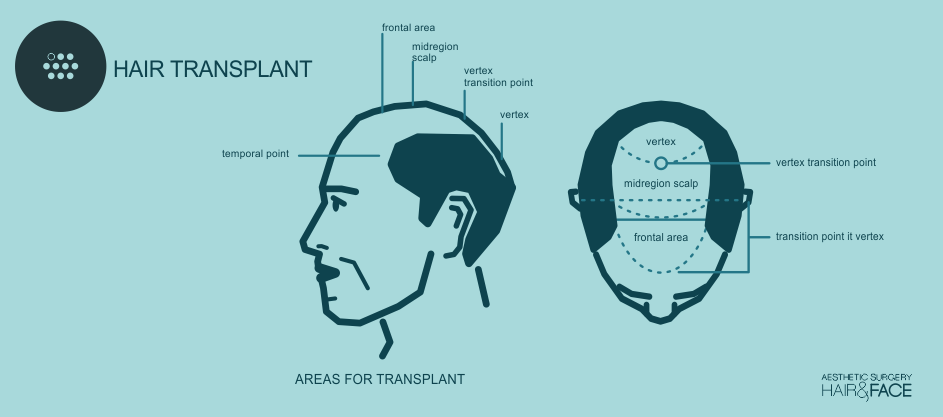
HAIR TRANSPLANT
It is an intervention which takes hair from the posterior part of the head and it is transferred to the area that suffers hair loss. The back part and the laterals of the scalp with baldness are known as the donor and dominant hair, and it’s a type of hair that will continue to grow for life in the majority of men, this way, the transplant of this hair to the balding area won’t affect its rowing capacity.
The donor dominance is the scientific base for the success of the hair transplant. In Japan, Dr Okuda described for the first time the use of transplanted hair to transplant eyebrows and eyelashes with scars. Orentreish in 1959 published the first report about hair transplant surgery.
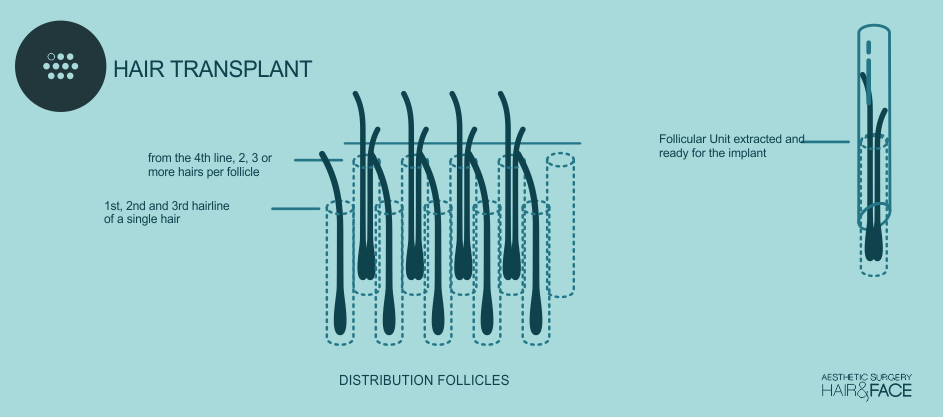
This surgery has advanced in enormous steps in the last decade, thanks to its use of the hair grafts with different root thickness, when the time to use the renovated instruments arrives, the hair restoration surgeons can provide a nearly perfect aspect of the hair, the hair graft of only one hair achieves a more natural and fine aspect and its used to obtain the first line of implantation. Micrografts are small grafts that contain two or three hairs which are situated behind the first line and offer a hair density that will gradually increase. Finally, the mini-grafts contain four or more airs and we place them quite behind the hairline. This way these types of hairs of which the surgery is based upon, are combined in a natural way with density that a great variety of grafts can offer.
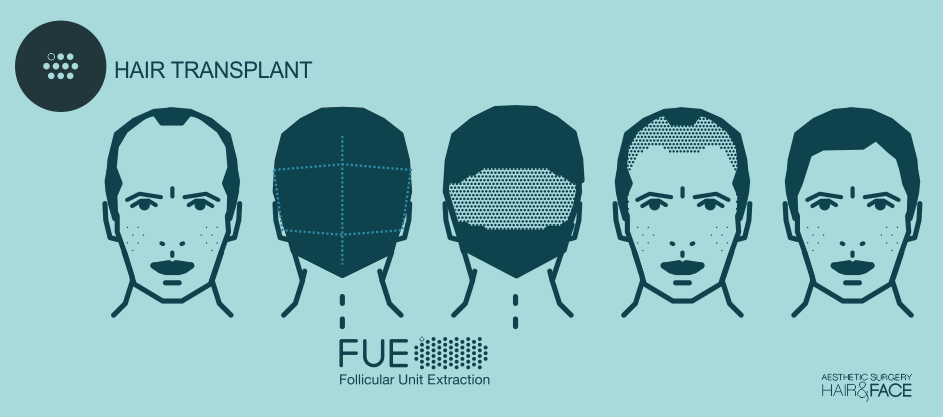
THE FUE TECHNIQUE OR FOLLICULAR UNIT EXTRACTION TECHNIQUE
With this technique, the most natural results are achieved and it allows the surgeon to implant a great amount of hair with the smallest possible incisions. The follicular units are extracted one by one, respecting the surrounding tissue. There are no cuts with a scalpel or posterior stitches. The left marks are so microscopic to the naked eye that the patient, if wishes to do so in the future can have their hair shaved. All anaesthetic is local, there isn’t any general anaesthetic. The patient is awake the whole time and the recovery is very quick, in only three days you can return to work.
SECONDARY EFFECTS
They are slight, they consist in a light pain or discomfort after the operation, possible inflammation which can reach to the eye area, the forming of scabs over the rafts will disappear in a week after the procedure.
Problems of bleeding or infection are very infrequent.
Modern hair transplant surgery is comfortable, predictable and the majority of the patients are very happy with the results. However, hair loss is a life process and the majority of men will develop male-pattern baldness until 40 or 45 years old.