An indication for this intervention is big and voluminous breasts that cause physical and psychological problems for the patient.
The procedure
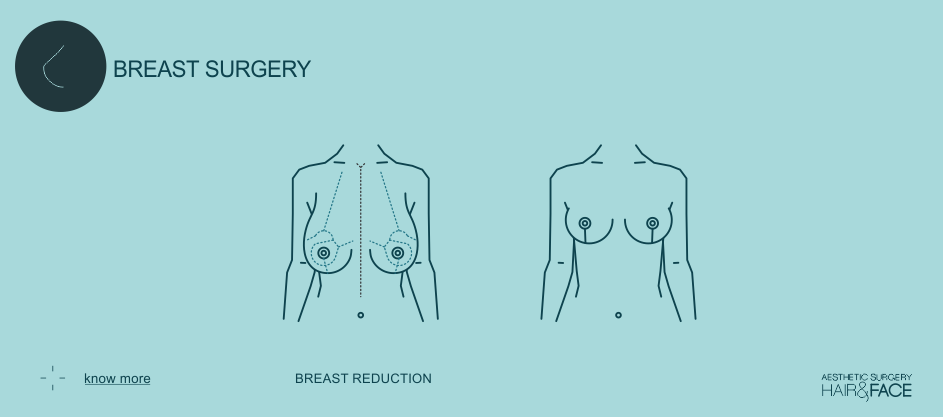
Fat, gland and skin are surgically removed; this achieves to shrink the breast and give them projection. The areola-nipple complex is positioned higher and the new breast is closed with some scars that vary from a simple periareolar, a vertical or an inverted T type.
The process lasts between 2 and 4hours
General anaesthetic is needed and one night admission at the clinic.
Post-operation
It’s a little painful;
During post-operation there will be inflammation and one or more bruises.
You shouldn’t do any brusque movements or a lot of effort, and avoid heavy lifting during the first few days.
Shower in 48hours
Back to work on the seventh day
The stitches are removed in 20days
There can be difficulty with breastfeeding.
The scars are visible.
Women who ask for this procedure have thought about their decision carefully of submitting to surgery and their desire is driven by themselves.
These women incorporate their new breasts to their body image quickly and they adjust fast to their new appearance.
The operation lasts between 2 and 4 hours, and general anaesthetic is required.
Fat, glandular tissue and skin are surgically removed.
Following a reduction, the breasts appear smaller.
The results are normally permanent, but the breasts can increase in size due to weight gain or if there are hormonal changes.
The inconveniences because of excessive mammary volume are of two kinds:
Physical inconveniences: neck pain, back and shoulder pain, pain in the mammary. Maceration and infection in the infra-mammary region.
Secondary neurological after effects and neck problems.
Difficulty in finding their clothes size and clothes that is attractive.
Psychological troubles: embarrassment, feelings of guilt, lack of physical attraction and loss of sexual attraction.
Technique types
Vertical mamoplasty
This technique tightens and reduces the breasts; fat is extracted and reduces the mammary ptosis tissue via resections in the lower and central part of the breast.
The width of the breast is reduced horizontally, and its shortened in a vertical direction and the infra-mammary fold is lifted, this makes the breasts appear raised and younger.
Superior pedicule technique
This procedure extracts the gland from the inner and lateral areas that provides an excellent reduction for the patient with moderate hypertrophy which requires reductions of 500 to 2000grams.
Double pedicule technique
This technique extracts the mammary gland from the inferior, lateral and superior lateral regions to reduce and tightens the breasts.
It is safe because it protects the intercostals and main blood vessels.
The mammary tissue stays less prone to postoperative ptosis
Free nipple graft
This is used in very big and hypotrophy breasts
It is a combined resections of the lateral and inner mammary with a free areola-nipple implant,which produces less incisions of the breast parenchyma with less internal scarring, making it easier for postoperative mammary tests for nodules and tumours.
Postoperative care
The patient leaves surgery with a compression bandage that should be kept on for 48hours.
Two days after the surgery, the compression bandage will be removed in the consulting room, and will be shown the result.
All activities that require lifting the arms over the head should be avoided for 4 to 6 weeks
No smoking from 15 days before the operation.
The sensation in the mammary will be reduced during the first weeks or months after the reduction. The patient shouldn’t be alarmed about this.
Problems and complications
All surgical procedures run inherent risks which include haemorrhage and infection.
The haematoma occurs in 1.5% of all cases.
Infection has an incidence rate of 2.2%
There is nerve injury with loss of sensitivity in 5% of cases.
Breastfeeding can be difficult
Necrosis is rare
Scars can be extensive.
